
#ABCD MATRIX CODE#
Your code should produce the same results as OS if you set it to model the whole system though, that’s a basic sanity check of your algorithm.Distribution-Rankings-For-of-Cascaded-ABCD-Matrix-Elementsĭistribution Rankings For of Cascaded ABCD Matrix Elements Considering both Magnitude and Phase file descriptions: What’s lost is the optical path length added or subtracted, which is why ABCD surfaces are not useful for imaging purposes ABCDs should only ever work with real ray data: measured (real) position and angle on the left and measured position and angle of the right. Aberration theory predicts a ray’s location incorrectly, and for some reason lost to history we consider the real ray location to be ‘aberrated’ with respect to the theory. These are exactly the same thing in the context of the ABCD approachĪnother way of thinking about this is that distortion is only an ‘aberration’ because it disagrees with aberration theory. I cannot see what the distinction is that you are making between ‘ray mapping’ and ‘distortion’. ABCD simply maps what’s on the object side to what’s on the Image side of whatever range of surfaces you want to describe. Similar in Python we can obtain value for ABCD Matrix shown in Image 3. In this Image 2, we can see the ABCD Matrix value in Matlab output console uisng MATLAB-API Interactive extension. Using these values to calculate A,B,C and D Values for Ray Transfer Matrix. We can export angle of incidence and angle of refraction using PATY Operand and Height of incidenct ray and Height of refracted ray using PARY inYZ Plane to a variable in Matlab. In ray transfer (ABCD) matrix analysis, an optical element a thick lens gives a transformation between (Y1,theta1) at the input plane and (Y1_p,theta1_p) when the ray arrives at the output plane. As we have PARY or PAXY operands for showing the height of Ray in X or Y -coordinate respectively and PATY shows tangent of the angle the paraxial ray makes in the Y-Z plane after refraction. We can calculate ray transfer matrix element by knowing Height of incidenct ray,Height of refracted ray ,angle of incidence and angle of refraction. My colleague has an idea of doing using operands. In OpticStudio, we can calculate the Ray transfer (ABCD) matrix using ZOS API(MATLAB and Python Interactive Extension). The grid distortion plot shows the linear grid, and then marks the actual chief ray intercept for a ray with the same linear field coordinates with an "X" for each point on the grid. If the image surface is rotated, such that a y object coordinate images to both an x and a y image coordinate, the ABCD matrix will automatically account for the rotation.

The use of an ABCD matrix allows for coordinate rotations. The ray coordinates in image space for the very small field of view are used to determine the ABCD matrix components. Where θr is the maximum radial field angle at the corner of the field.
#ABCD MATRIX FULL#
Because object height is linear with the tangent of the field angle, the full width of the field when angles are used to define the field is given by OpticStudio allows selection of which field position to use for reference.By default, OpticStudio sets the corner of the field grid in object space to be at the maximum radial field distance.
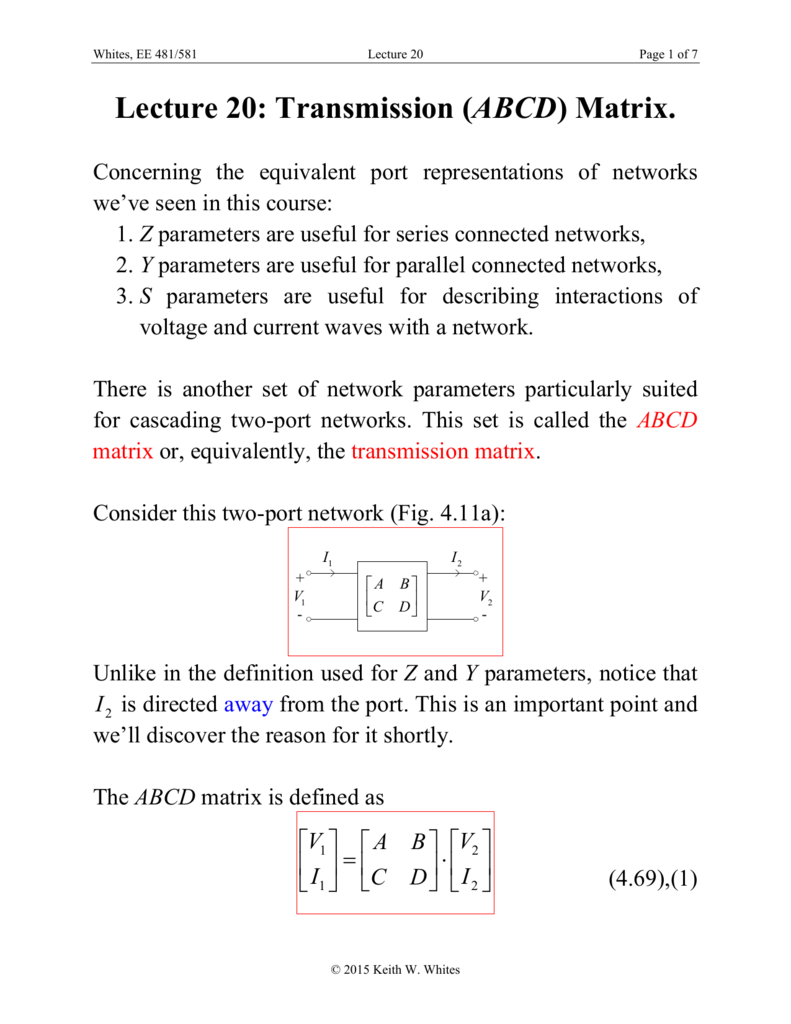
Usually, this is the center of the field of view. To compute the ABCD matrix, OpticStudio traces rays over a very small region centered upon the reference field position.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
